Digoxigenin
Digoxigenin
DIG (digoxigenin) is a small molecule used as a non-radioactive label in molecular biology applications. It is often attached to nucleic acids like DNA or RNA for detection in hybridization assays. DIG is preferred for its stability, low background signal, and strong binding affinity to anti-DIG antibodies, allowing for highly sensitive detection. In Point-of-Care Testing (POCT), DIG-labeled oligos can be used in DNA amplification, with the amplified products detected via lateral flow assays using anti-DIG antibodies. This system provides a simple and effective method for visual detection, making it suitable for resource-limited settings or rapid diagnostic tests in clinics. DIG-antibody does not cross-react with digoxin, digitoxin, ouabain.
Validation Data
EC50 data
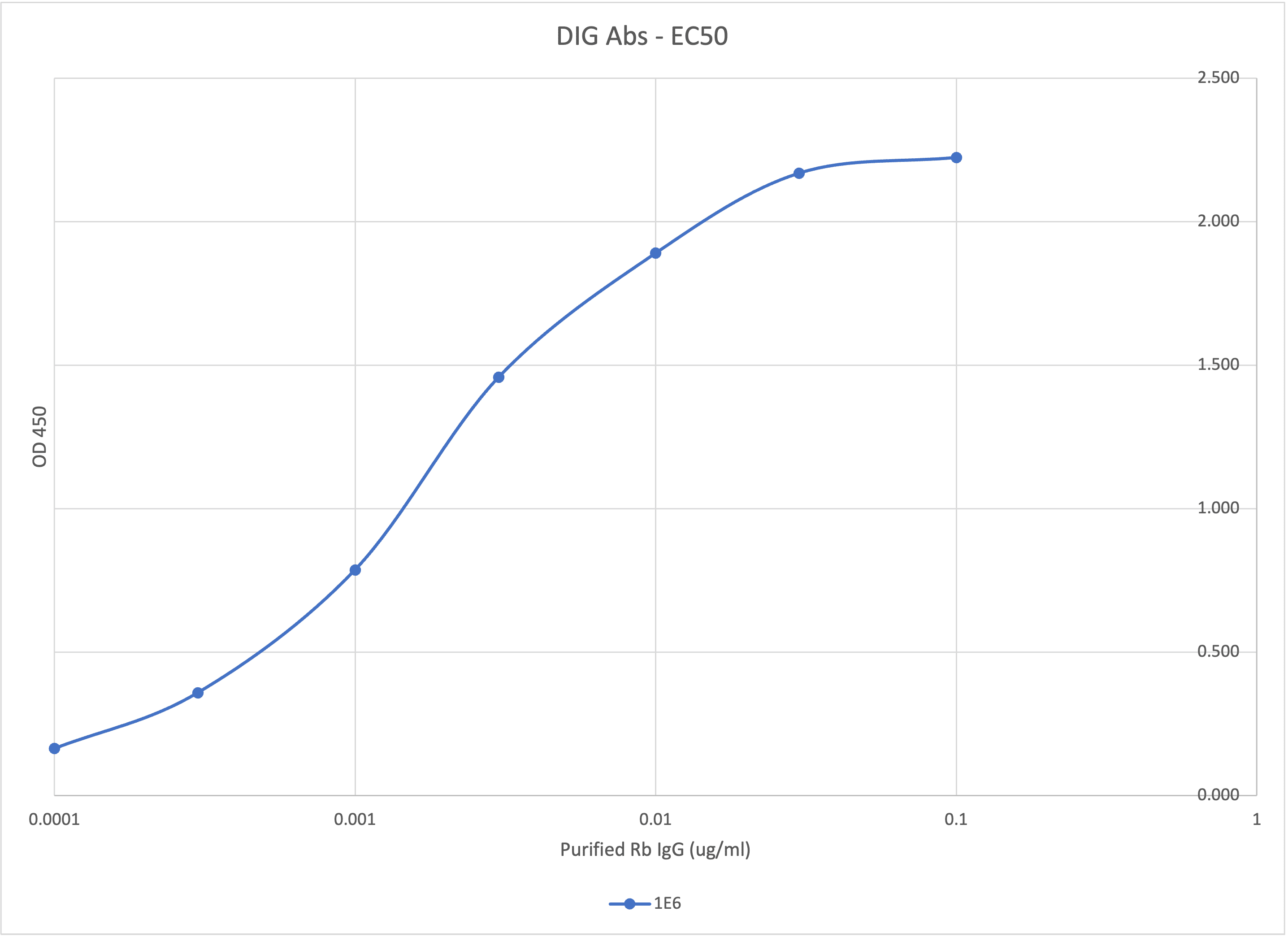
EC50 Determination of DIG antibody. The graph illustrates the dose-response curve for the DIG antibody.
Kinetics evaluation
These kinetics demonstrate the high affinity and strong binding stability of the DIG-1E6 antibody, making it an excellent choice for sensitive detection applications.