Llama Monoclonal Antibody
With our novel Single Plasma Cell Interrogation (SPIN®) Technology, single chain antibodies are isolated from individual plasma cells of immunized llamas and are expressed in mammalian cells, allowing them to be functionally analyzed.
Benefits
Accessibility
VHH single domain antibodies are only 15kD in size, compared to about 150kD for typical immunoglobulins. The smaller size makes it easier to penetrate tissues and gives them access to “hidden” epitopes while readily crossing the blood-brain barrier.
Solubility
Single domain antibodies display a marked reduction of in hydrophobicity, which in turn leads to a very high solubility.
Stability
VHH antibodies are extremely stable and resistant to both high acidity and high temperature. They’re even able to fold back into a functional protein after denaturation.
Engineerable
VHH antibodies are pure monomers, offering fast-track lead optimization and engineering to bi-specific nanobodies.
Benefits
Accessibility
VHH single domain antibodies are only 15kD in size, compared to about 150kD for typical immunoglobulins. The smaller size makes it easier to penetrate tissues and gives them access to “hidden” epitopes while readily crossing the blood-brain barrier.
Stability
VHH antibodies are extremely stable and resistant to both high acidity and high temperature. They’re even able to fold back into a functional protein after denaturation.
Solubility
Single domain antibodies display a marked reduction of in hydrophobicity, which in turn leads to a very high solubility.
Engineerable
VHH antibodies are pure monomers, offering fast-track lead optimization and engineering to bi-specific nanobodies.
Why Llama?
Llama antibodies have all the characteristics we expect from mammalian immune systems. However, they also include a group of smaller antibodies that don’t correspond to anything seen in other animals. They are heavy chain dimers with an extensive antigen-binding repertoire. They lack the light chains altogether. Because of their small size, single chain antibodies raised against small enzymes such and can access their enzymatic active sites to provide potent enzyme inhibition.

Llama IgG Gene Structure
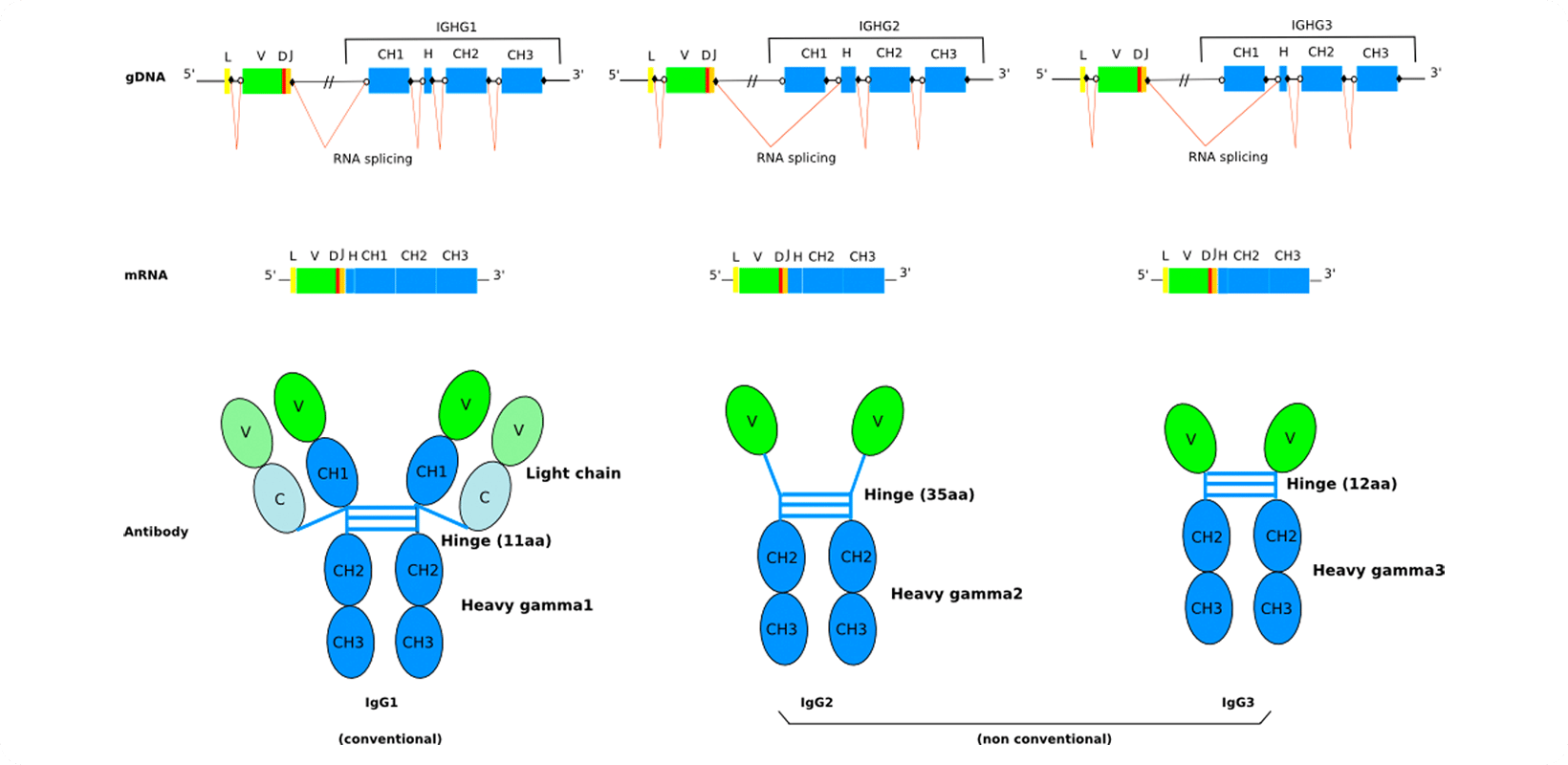
The Arabian camel (Camelus dromedarius) and the llama (Lama glama) have three IgG subclasses: the conventional IgG1 and the non-conventional IgG2 and IgG3.
What makes IgG2 and IgG3 different from its two counterpart? There’s a splicing defect in the CH1 exon which causes the CH1 domain to be absent in both the gamma 2 and gamma 3 chains. This leads to a striking difference from IgG1: a lack of light chains in IgG2 and IgG3.
Timelines
Llama Immunization

Isolation of Plasma Cells
Single domain library construction
Screening and selection
Deliverables
| Phase I | Timeline | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| Llama immunization | 4-6 months | ELISA data |
| Phase II | Timeline | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| Splenectomy and lymphocyte isolation | ||
| First screening with FACS (> a million B cells)
|
2 weeks | |
| Supernatant production, and Secondary screening | 4 weeks | ELISA data |
| Phase III | Timeline | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| 3 weeks | Purified Antibody |