Influenza B
Influenza B
Exonbio offers an expansive range of Influenza B IVD reagents for diagnostics including recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins for different strains of influenza B virus.
Influenza B
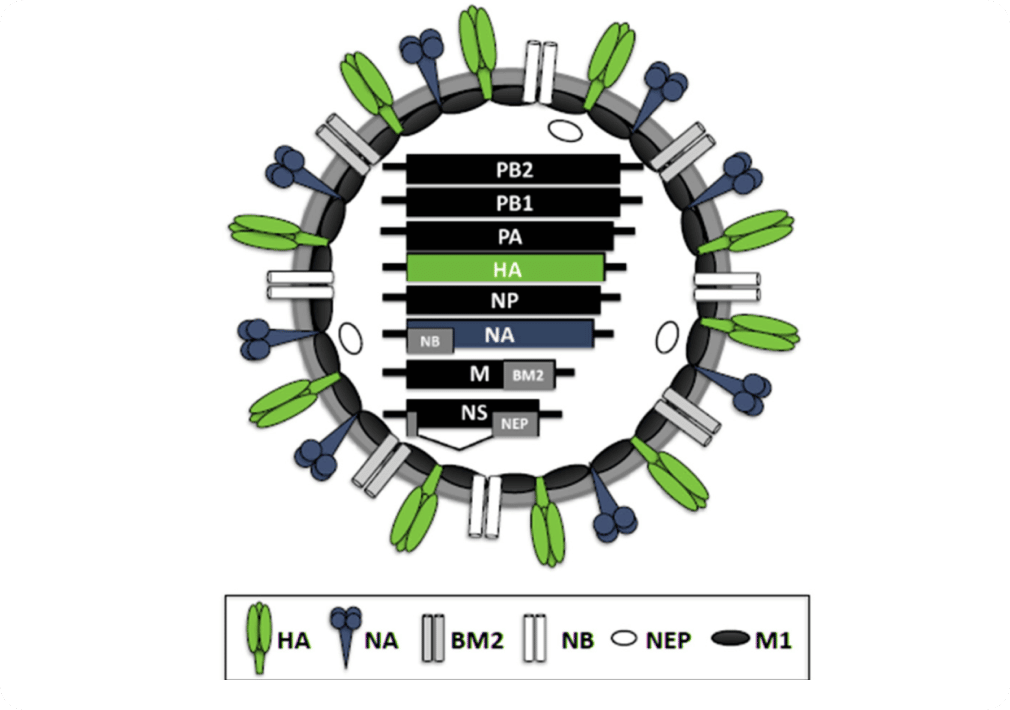
Influenza B viruses are separated into two distinct genetic lineages (Yamagata and Victoria) on the basis of differences in the HA glycoprotein. Influenza B viruses from both lineages have co-circulated during most influenza seasons since the 1980s.Influenza viruses undergo constant genetic change, which has substantial impact on induced immunity and considerations for vaccine composition. Two main types of changes are recognized. Point mutations and recombination events occur in the viral genome, resulting in constant emergence of new virus variants. This phenomenon is termed “antigenic drift”. While it occurs among both influenza A and B viruses, influenza A viruses undergo antigenic drift more rapidly than influenza B viruses. Frequent emergence of antigenic variants through antigenic drift is the virologic basis for seasonal influenza epidemics, and necessitates consideration of adjustment of vaccine viruses each season.