C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Antibody, 1H1
$350.00 – $1,500.00
| Product Name | C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Antibody, 1H1 |
| Catalog Number | EX-1H1CREX-1H1CR |
| Immunogen | Native C-Reactive Protein |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Preparation | Recombinant monoclonal antibody expressed in HEK293F cells and purified by protein A affinity chromatography. |
| Applications | Any application that detects RSV virus, pseudo virus, and RSV native nucleocapsid protein. Does not detect denatured nucleocapsid protein. |
| Reactivity | RSV nucleocapsid protein |
| Isotype | rabbit IgG, kappa |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Purification | Protein A affinity chromatography |
| Storage buffer | PBS |
| Storage conditions | For long term storage, the antibody should be stored at -20℃ and is stable for 12 months from the date of receipt. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. For short term storage, keep at 4oC for a week should be fine. |
| Application Dilution | 1:1,000-1:100,000 (platform dependent, customers must test the optimal concentration on their own platform) |
Additional information
| Size | 100µg, 1mg |
|---|
Background information
Understanding C-Reactive Protein (CRP) in Immunoassays
What is C-Reactive Protein?
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a protein made by the liver and released into the bloodstream in response to inflammation. It plays a crucial role in the body’s immune response by helping to fight infection and heal injuries.
Why Measure CRP?
Measuring CRP levels through immunoassays is important for several reasons:
• Detecting Inflammation: Elevated CRP levels can indicate inflammation in the body, although they do not pinpoint the exact cause or location.
• Diagnosing and Managing Diseases: CRP is a valuable tool in diagnosing and monitoring conditions like bacterial infections, autoimmune diseases, and systemic inflammations.
• Assessing Cardiovascular Risk: High-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) tests can help evaluate the risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes.
• Monitoring Treatment Efficacy: Changes in CRP levels can indicate how well a patient is responding to treatment for inflammatory conditions.
• Differentiating Infections: CRP levels can sometimes help differentiate between bacterial and viral infections.
How Does CRP Testing Work?
CRP testing is typically done through a blood test. The process involves:
1. Blood Sample Collection: A small blood sample is taken from a vein in your arm.
2. Analysis in Laboratory: The sample is analyzed using immunoassay techniques to measure the CRP level.
3. Interpreting Results: Your healthcare provider interprets the results, considering other tests and your overall health status.
Understanding Your Results
• Normal Range: Typically, a normal CRP level is below 10 mg/L, but this can vary.
• Elevated Levels: Higher levels might indicate inflammation or infection, but further tests are often required for a specific diagnosis.
Datasheet
| Datasheet | Download |
Validation data
| Validation data | Download |
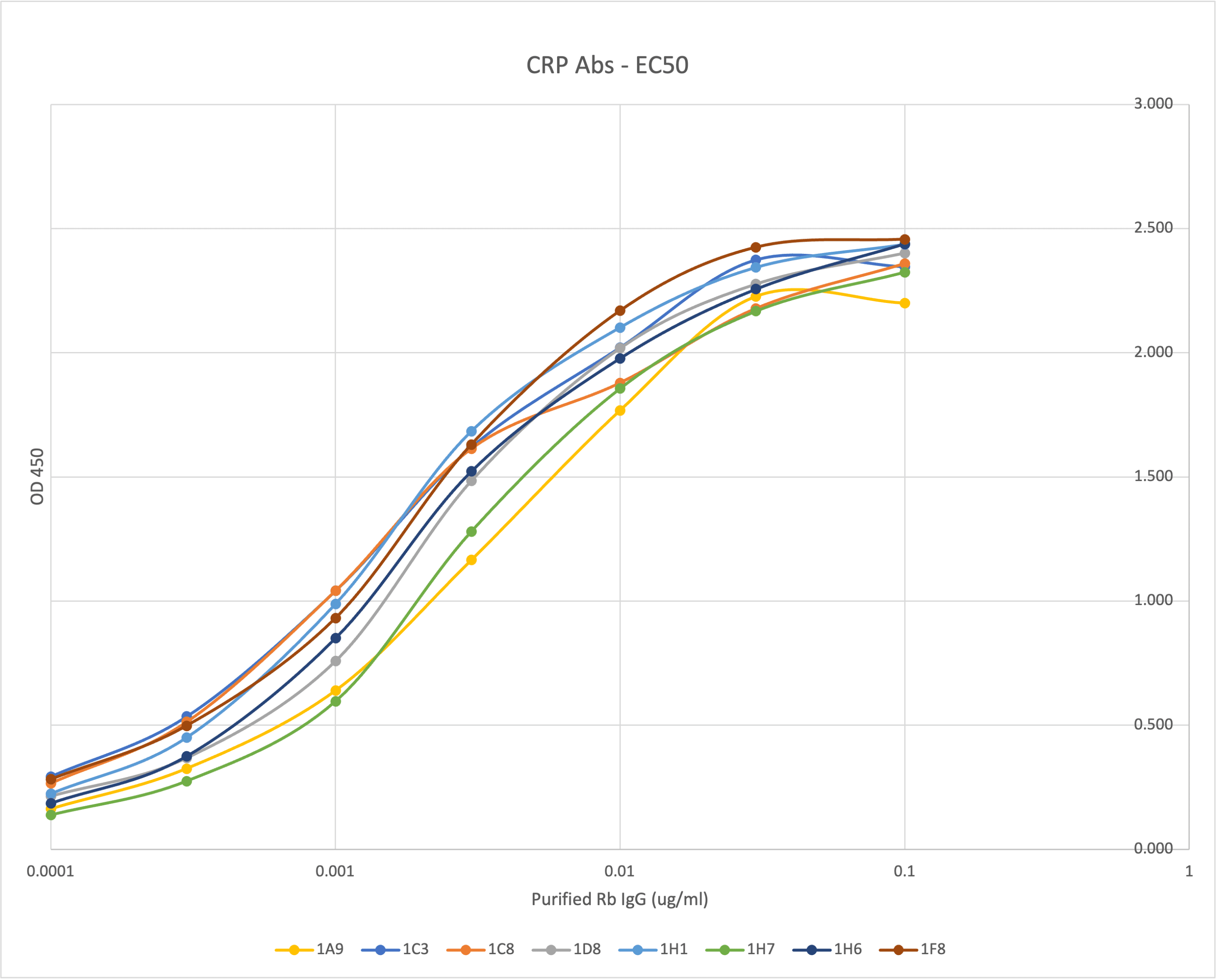
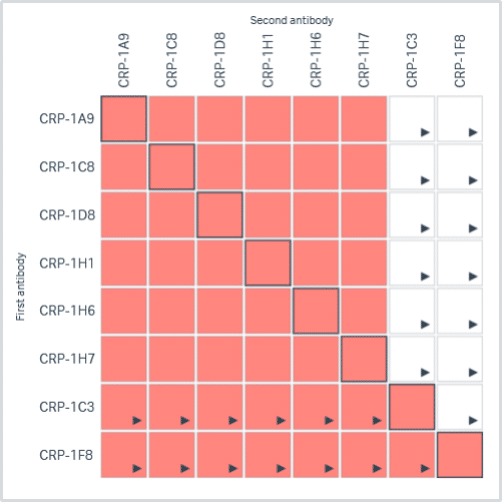
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.